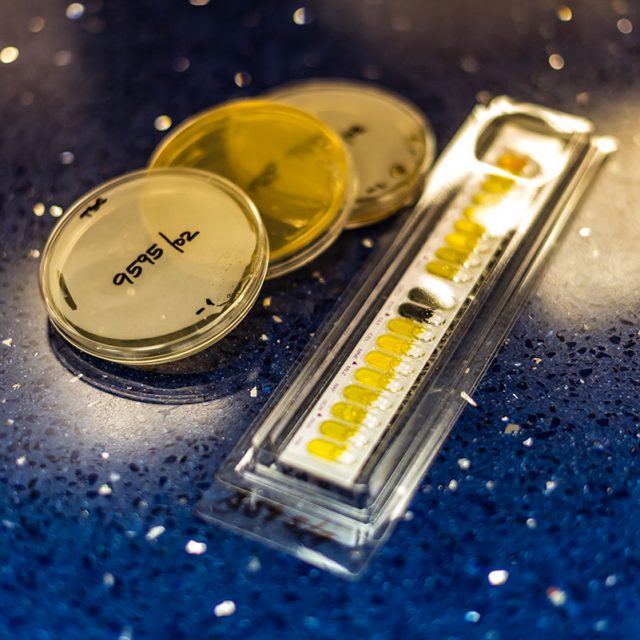
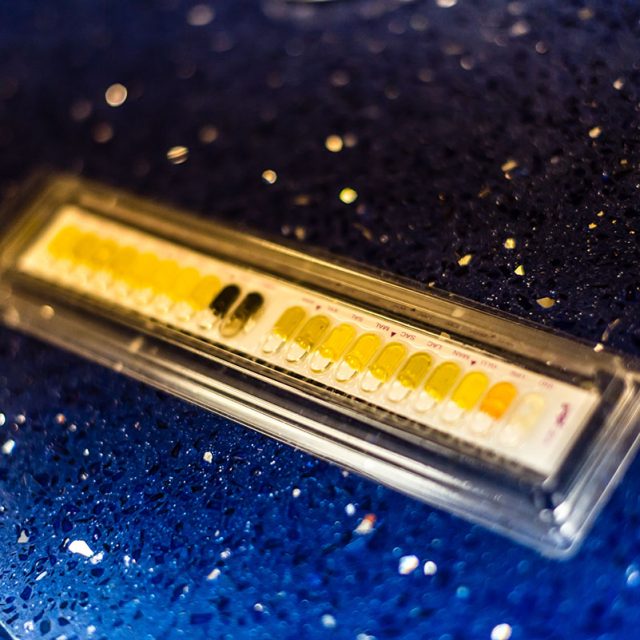
The Department of microbiological and molecular biology research of the Institute carries out microbiological analyses of food safety, safety of animal feed, food dietary products, general purpose items and samples of surfaces in contact with food.
Department uses 65 accredited methods in its work, covering all known pathogenic microorganisms in food (Salmonella, Escherichia, Clostridia, Staphylococci, etc.), but also the causes of food spoilage. The methods are mainly standardized to ensure the recognition of test results in national and international food trade. Annually around 31,000 samples are analysed.
In addition to the research related to food safety, staff of the Department has been engaged, for 15 years, using molecular biological methods, and are called as experts, in cases of food counterfeiting -usually in the form of adding low value parts of tissue of certain types of animals without stating the composition.
Following the request of state authorities, the Department conducts tests on the presence and quantification of GMO content in food, animal feed and dietary products.
Associates are involved in solving of problems realted to export of Serbian berry fruit on the EU market, the USA and Japan, so we are currently the only accredited laboratory in the Republic of Serbia (in the Balkans) for testing the presence of norovirus and hepatitis A virus.
In order to keep pace with the developed countries of the EU, and to maintain competitiveness, the Department has a leading, coordinating and promotional role in the following activities:
- Achieving national referentiality testing of certain food-borne pathogens;
- Monitoring yersiniosis, vibriosis, botulism and calicivirus and prevalence of hepatitis A in food and feed;
- Improvement of microbiological parameters in the hygiene of the slaughter process, meat cutting and processing;
- Development and establishment of a monitoring program for fecal contaminants and Listeria monocytogenes in meat industry facilities;
- Improvement of communication about the risks to the safety of food (meat) in the mutual relation state bodies-industry-consumers;
- Development, optimization and validation of methods for testing new foodborne pathogens, including application of mass-spectrometric chromatography for identification of microorganisms;
- Development and establishment of an integrated system of monitoring of zoonoses and zoonotic foodborne pathogens on the territory of the Republic of Serbia (especially microorganisms from the genera Salmonella, Campylobacter, Listeria monocytogenes, and Shiga-like toxigenic Escherichia coli), monitoring of their resistance to antimicrobial agents and the exchange of data related to zoonoses and their pathogens in the food/meat chain;
- Analysis of microbiological risks and categorization of risk by the principle “type of food/food-pathogen”